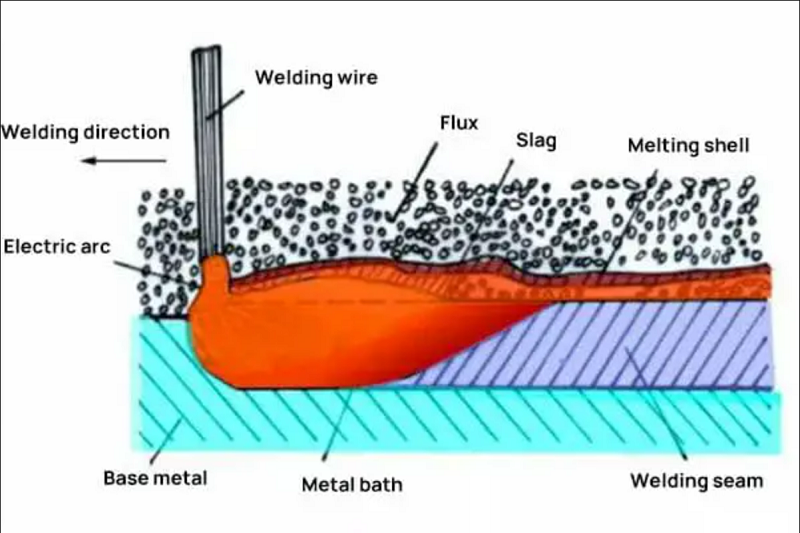
– FLUX–
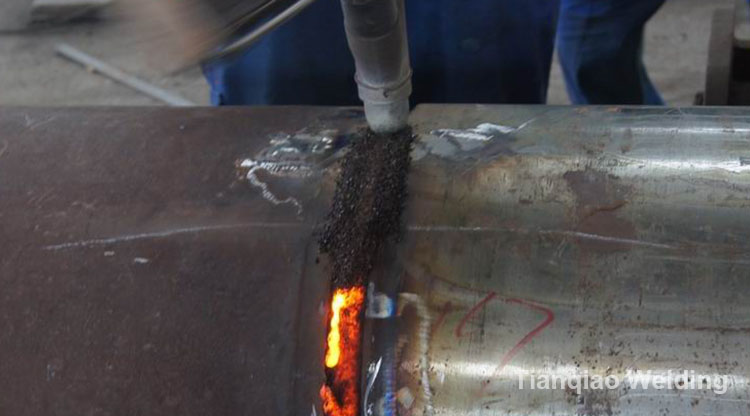
Flux is a granular welding material. During welding, it can be melted to form slag and gas, which plays a protective and metallurgical role on the molten pool.
Constituent
Flux is composed of marble, quartz, fluorite and other ores and titanium dioxide, cellulose and other chemicals. Flux is mainly used for submerged arc welding and electroslag welding. When used for welding all kinds of steel and non-ferrous metals, it must be reasonable use with the corresponding welding wire so that to get a satisfactory weld.
Classification
There are many classification methods of flux, according to the use, manufacturing method, chemical composition, welding and metallurgical properties of the classification, but also according to the pH of flux, flux granularity classification. No matter which kind of classification method, only reflect the characteristics of flux from a certain aspect, it cannot include all the characteristics of flux. The commonly used classification methods are:
1. Neutral flux
Neutral flux refers to the flux that does not significantly change the chemical composition of the fused metal and the chemical composition of the welding wire after welding. Neutral flux is used for multi-pass welding, especially for the welding of the base metal with a thickness greater than 25mm.Neutral flux has the following characteristics:
a. The flux basically does not contain SiO2, MnO, FeO and other oxides.
b. Flux has no oxidation effect on weld metal basically.
c. When welding base metal with severe oxidation, pores and weld cracks will be produced.
2. Active flux
Active flux refers to the addition of a small amount of Mn, Si deoxidizer flux. It can improve the resistance to porosity and crack. Active flux has the following characteristics:
a. Due to the deoxidizer, Mn and Si in the molten metal will change with the arc voltage. The increase of Mn and Si will increase the strength of the molten metal and reduce the impact toughness. Therefore, arc voltage should be strictly controlled when multi – pass welding.
b. Active flux has strong porosity resistance.
3. Alloy flux
Alloy flux added more alloy components for the transition of alloying elements, most of the alloying flux is sintered flux. Alloy flux is mainly used for welding of low alloy steel and wear-resistant surfacing.
4. Melt flux
Melt flux is the raw materials of various minerals mixed in accordance with the given ratio, heated to more than 1300 degrees, melted and stirred evenly, and then cooled in water to granulate. After drying, grinding, screening, packaging use.
The brand of domestic melting flux is expressed by “HJ”. The first digit after it indicates the content of MnO, the second digit indicates the content of SiO2 and CaF2, and the third digit indicates different brands of the same type of flux.
5. Sintering flux
It is dry mixed according to the given proportion of ingredients, and then adding binder (water glass) for wet mixing, and then granulation, and then sent to the drying furnace curing, drying, and finally sintered by about 500 degrees.
The brand of domestic sintered flux is represented by “SJ”, the first digit after that represents the slag system, and the second and third digits represent different brands of the same slag system flux.
Post time: May-04-2023