The welding electrode is a metal rod that is melted and filled at the joint of the welding work-piece during gas welding or electric welding. The material of the electrode is usually the same as the material of the work-piece.
Here we come to understand how with the welding electrode is composed of: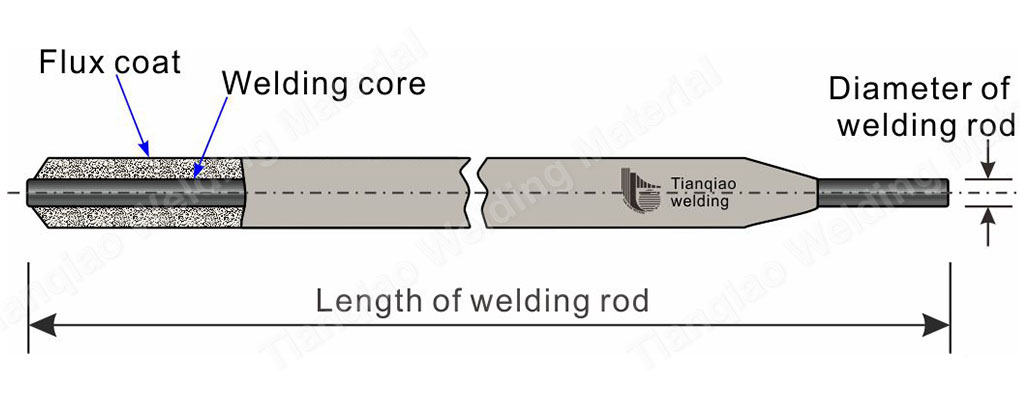
Figure 1 Structure of Tianqiao welding electrode
The welding electrode is a melting electrode coated with a coating for arc welding of the welding rod. It is composed of a coating and a welding core.
The metal core covered by the coating in the welding rod is called the welding core. The welding core is generally a steel wire with a certain length and diameter.
Figure 2 Core of Tianqiao welding electrode
Two functions of the core
1. Conduct welding current and generate arc to convert electrical energy into heat.
2. The welding core itself melts as a filler metal and fuses with the liquid base metal to form a weld. When welding with an electrode, the core metal occupies a part of the entire weld metal. Therefore, the chemical composition of the weld core directly affects the quality of the weld. Therefore, the steel wire used as the core of the electrode has its brand and composition separately specified.
Electrode coating refers to the coating layer applied on the surface of the welding core. The coating is decomposed and melted in the welding process to form gas and slag, which play a role in mechanical protection, metallurgical treatment, and improvement of process performance.
Figure 3 Coating of Tianqiao welding electrode
The composition of the coating includes: minerals (such as marble, fluorspar, etc.), ferroalloys and metal powders (such as ferromanganese, ferro-titanium, etc.), organic substances (such as wood flour, cellulose, etc.), chemical products (such as titanium dioxide, water glass, etc.). Electrode coating is an important factor in determining the quality of welds.
Main functions of coating in the welding process
1. Improve the stability of arc combustion:
The uncoated electrode is not easy to ignite the arc. Even if it is ignited, it cannot burn stably.
2. Protect the weld pool:
During the welding process, oxygen, nitrogen and water vapor in the air penetrate into the weld seam, which will have an adverse effect on the weld seam. Not only formation of pores, but also reduce the mechanical properties of the weld, and even cause cracks. After the electrode coating is melted, a large amount of gas is generated covering the arc and the molten pool, which will reduce the interaction between the molten metal and the air. When the weld is cooled, the melted coating forms a layer of slag, which covers the surface of the weld, protects the weld metal and cools it slowly, reducing the possibility of porosity.
Three, to ensure that the weld is deoxidized and desulfurized and phosphorus impurities
Although protection is carried out during the welding process, it is still inevitable that a small amount of oxygen will enter the molten pool to oxidize the metal and alloy elements, burn the alloy elements, and reduce the quality of the weld. Therefore, it is necessary to add a reducing agent (such as manganese, silicon, titanium, aluminum, etc.) to the electrode coating to reduce the oxides that have entered the molten pool.
4. Supplement alloying elements for the weld:
Due to the high temperature effect of the arc, the alloying elements of the weld metal will be evaporated and burnt, which will reduce the mechanical properties of the weld. Therefore, it is necessary to add appropriate alloying elements to the weld through the coating to compensate for the burnt loss of the alloy elements and to ensure or improve the mechanical properties of the weld. For welding of some alloy steels, it is also necessary to infiltrate the alloy into the weld through the coating, so that the weld metal can be close to the metal composition of the base metal, and the mechanical properties can catch up with or even exceed the base metal.
5. Improve welding productivity and reduce spatter:
The electrode coating has the effect of increasing the droplet and reducing the spatter. The melting point of the electrode coating is slightly lower than the welding point of the core. However, because the welding core is in the center of the arc and the temperature is relatively high, the welding core melts first, and the coating melts a little later. At the same time, since the metal loss caused by spatter is reduced, the deposition coefficient is increased, and the welding productivity is also improved.
Post time: Jun-01-2021


